As a business owner, you've seen the headlines. A ransomware attack can feel like a distant, big-corporation problem, but the reality is that cybercriminals are increasingly setting their sights on small and medium-sized businesses right here in Western Pennsylvania and Eastern Ohio. They know you're busy, your IT resources are stretched thin, and a successful attack could bring your operations to a grinding halt.
The good news? Preventing a ransomware attack isn't about building an impenetrable digital fortress. It’s about being prepared, proactive, and making your business a harder, less profitable target than the next one. This guide isn't about fear; it’s a practical, no-jargon playbook to help you protect the business you've worked so hard to build.
Building Your Ransomware Prevention Strategy

If you're running an SMB, the threat of ransomware isn’t just a news story—it's a direct threat to your livelihood. Whether you're in manufacturing, professional services, or healthcare, an attack can lock up critical files, halt production, and damage your reputation with customers who trust you with their data.
Cybercriminals love SMBs because they're betting you have a lean IT staff and a budget stretched across a dozen other priorities. They know a successful attack can bring a manufacturing line to a standstill, lock up sensitive patient records, or stop a professional services firm in its tracks.
But this isn't a scare tactic. As a trusted IT advisor to businesses in this region, I understand the daily pressures you face. Cybersecurity can feel like just one more complex task on an already packed to-do list.
My goal here is to demystify ransomware prevention and give you a clear, practical roadmap. We'll focus on the high-impact steps that deliver the best protection for your investment and truly secure your business.
The Four Pillars of Ransomware Defense
To build an effective defense, you have to understand the modern threat landscape and learn how to defend your organisation from ransomware attacks from the ground up. In my experience, a strong strategy is always built on four core pillars that address both your technology and your people.
Think of these four pillars as the non-negotiable layers of your defense.
| The Four Pillars of Ransomware Defense for SMBs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Pillar | Core Action | Why It's Critical for SMBs |
| Technical Controls | Implement foundational security tools like patching, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and modern threat detection. | These controls create essential barriers that block the most common automated attack methods used against small businesses. |
| Backup & Recovery | Establish a robust, tested backup system following the "3-2-1" rule (3 copies, 2 media types, 1 offsite). | This is your ultimate safety net. A reliable backup makes the ransom demand irrelevant, allowing you to restore operations on your own terms. |
| Employee Training | Turn your team into a "human firewall" with ongoing education on phishing and social engineering. | Most breaches start with a human element. An aware employee is one of your most effective and cost-efficient lines of defense against initial intrusion. |
| Incident Response | Create a clear, simple plan outlining who to call and what steps to take the moment an incident is suspected. | When an attack happens, chaos is the enemy. A pre-defined plan ensures a swift, organized response, minimizing damage and downtime. |
Focusing on these four pillars provides a clear framework. A common mistake I see business owners make is treating ransomware prevention like a one-time project. It's not. It's an ongoing process of managing risk.
By consistently reinforcing these areas, you transform ransomware from a potential disaster into a manageable business challenge, securing your company's future.
Building Your Human and Technical Defenses

Here's a truth I’ve learned from years on the front lines of IT in Western PA and Eastern OH: ransomware attackers rarely kick down the digital front door. They're much more likely to be invited in. They prey on two weak points almost every business has: good old-fashioned human error and unsecured digital doorways.
A real defense starts by locking down both. First, your people. No amount of fancy security gear can stop an employee from clicking a convincing but malicious link. That’s why we start by building a "human firewall." Then, we add technical controls that make it nearly impossible for a stolen password to do any damage.
Turning Your Team Into a Human Firewall
Let’s be honest. Most cybersecurity training is a boring slideshow that everyone forgets the moment they leave the room. To build a true human firewall, you need an engaging and continuous program that trains your team to be healthily skeptical of every email and message they receive.
The most effective way to do this is with phishing simulations. We send controlled, safe emails to your team that mimic the real attacks hitting businesses in Pittsburgh and Youngstown every day. When someone clicks, they aren't punished. Instead, they get immediate, on-the-spot training that points out the exact red flags they missed.
This works because it’s learning by doing, right when it's most relevant. It completely changes the game from a passive lecture to an active, hands-on experience.
Key Takeaway: An employee who has been safely "phished" in a simulation is far less likely to fall for a real attack. It builds the right kind of muscle memory for spotting threats in the wild.
For a deeper dive, check out our guide on phishing attack prevention for small businesses in Pittsburgh and Youngstown. It’s full of practical tips you can use right now.
Make sure your training teaches everyone to spot these common red flags:
- Sudden Urgency: Emails demanding immediate action, threatening to lock an account, or offering a deal that’s too good to be true. These should set off alarm bells.
- Suspicious Senders: Get your staff in the habit of hovering over the sender's name to see the real email address. It’s often just slightly off, like "Microsoft-Support@mail-security-alert.com" instead of a legitimate Microsoft domain.
- Generic Greetings: Big companies you do business with will almost always use your name. If you see "Dear Valued Customer" or "Hello User," be suspicious.
- Weird Links: Always hover your mouse over a link before you click. The little preview box will show you the real destination. If it looks strange or doesn't match where the email claims to be from, it's a huge warning sign.
Why Multi-Factor Authentication Is Non-Negotiable
After building up your human firewall, the single most powerful technical control you can implement is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Think of MFA as a deadbolt on your digital door. Even if a cybercriminal steals an employee's password, that password is useless without the second piece of the puzzle—usually a code sent to their phone.
MFA isn't an optional extra anymore; it's a fundamental security requirement. It needs to be enabled on every critical system, no exceptions. This includes:
- Email Systems: Your Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace accounts are the keys to the kingdom for attackers.
- Remote Access: Any VPN or remote desktop connection must be locked down with MFA.
- Financial Apps: Protect your accounting software, payroll systems, and online banking logins.
- Admin Accounts: Any account with privileged access that can change system settings is a top priority.
The numbers don't lie. Industry data consistently shows that a significant percentage of ransomware incidents start with a compromised password. By enabling MFA on your key accounts, you reduce the risk of a successful account takeover by over 99%. That's a massive reduction in risk from one simple action.
I know what many SMB owners in manufacturing or professional services are thinking: "Won't this slow my team down?" The truth is, modern MFA solutions are incredibly slick. They use simple push notifications ("Approve/Deny") or biometrics, making the login process fast and painless. That minor inconvenience is a tiny price to pay for the massive security upgrade it delivers.
Securing Your Network with Patching and Segmentation
Even with a well-trained team and strong authentication, a determined attacker might still slip through. When that happens, your next layer of defense is what stands between a minor incident and a full-blown disaster. The goal shifts from keeping them out to stopping them from moving around once they're inside.
This is where two of the most foundational security practices—consistent software patching and smart network segmentation—make all the difference.
Think of an unpatched piece of software as a known, unlocked window to your business. Cybercriminals actively scan for these vulnerabilities because they offer a cheap, automated ticket into your systems. Likewise, a "flat" network where every computer can talk to every other computer is like an open-plan office for an attacker. Once they're in one cubicle, they can wander over to the CEO's office without anyone stopping them. Let's talk about how to lock those internal doors.
Closing the Door with Timely Patch Management
Every piece of software on your network—from your server's operating system to the accounting app your team uses daily—will eventually have security flaws discovered. When they are, developers release updates, or "patches," to fix them. Failing to apply these patches is one of the most common—and avoidable—mistakes I see businesses in our region make. It's a direct invitation for trouble.
A structured patch management process is non-negotiable for preventing ransomware. And no, this isn't just about running Windows Update. It’s a systematic process for keeping all your critical software current. If you want to dig deeper into the nuts and bolts, we have a whole guide on what is patch management. This process ensures you have a reliable way to identify, test, and deploy crucial updates before attackers can exploit the vulnerabilities they fix.
Expert Insight: Don't treat patching as a low-priority, "get to it when we can" IT task. It's a high-impact security function. The time between a patch being released and a criminal exploiting that flaw can be a matter of hours, not weeks.
The data backs this up. Recent industry reports show that a staggering number of successful ransomware attacks start by exploiting known, unpatched vulnerabilities. Globally, these known weaknesses were the entry point for a significant share of security incidents last year.
This is exactly why security experts recommend applying critical patches within 14 days and high-risk patches within 30 days. Hitting those timelines will dramatically lower your risk profile. You can read the full research on these ransomware trends if you want to see the raw numbers.
Containing the Damage with Network Segmentation
Now, let's talk about containing the "blast radius." If an attacker does get in, how do we stop them from taking down the whole company?
Network segmentation is the practice of dividing your company network into smaller, isolated sub-networks. It’s the digital equivalent of a submarine's watertight compartments—if one area floods, the breach is contained and the rest of the ship stays afloat.
For an SMB in Western PA or Eastern OH, this doesn't have to be some overly complex, enterprise-grade project. The core idea is simple: prevent a single compromised laptop from being able to infect your most critical servers.
Here are a few practical examples of how we implement this for our clients:
- Isolate Your Crown Jewels: Your main file server, database server, and domain controller should live on their own dedicated network segment. Only specific, authorized computers and users should be able to communicate with them. A user in the sales department shouldn't be able to directly access the server running your accounting software.
- Create a Guest Wi-Fi Network: This one is a no-brainer. Never allow visitors or personal employee devices onto your primary corporate network. A separate, isolated guest network is simple to set up and provides internet access without exposing your business systems.
- Separate Departments or Functions: For a manufacturing company in Youngstown, we'd place the shop floor equipment and control systems on a different network segment from the front office computers. This prevents a phishing attack on a sales PC from spreading to the machinery that actually runs your operations.
By implementing these segmentation strategies, you force an attacker who gains initial access to work much harder to find and encrypt your valuable data. You shrink their playground, making it far more likely that your security tools will detect and stop their activity before they can do widespread harm. It’s a powerful, proactive step in any serious ransomware prevention plan.
Implementing a Resilient Backup and Recovery Plan
If a ransomware attack is the disease, a rock-solid backup and recovery plan is the only reliable cure. When every other defense has failed, your ability to restore your data is the final backstop that makes a cybercriminal’s ransom demand completely irrelevant. It gives you the power to walk away and get your business back online without paying a single dime.
For SMBs across Western Pennsylvania and Eastern Ohio, this isn’t about having a dusty external hard drive in a closet. We're talking about a modern, resilient system built to withstand a direct assault. The industry gold standard for this is a framework known as the "3-2-1" rule.
Let’s break down what this means in practical terms for your business:
- Three Copies: You need your primary data plus at least two other backups.
- Two Different Media: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Store copies on at least two different storage types, like a local network device and a cloud service. This protects you if one type of media fails.
- One Copy Off-site: At least one backup must be physically separate from your office. Cloud backups are perfect for this. An off-site copy that is immutable (cannot be altered or deleted) or air-gapped (completely disconnected from your live network) is the game-changer against modern ransomware.
From Theory to Reality: The 3-2-1 Rule in Action
For a manufacturing firm in Youngstown or a law office in Pittsburgh, applying this rule is more straightforward than it sounds. A typical setup we recommend involves a local backup appliance for fast, on-site restores. That local backup is then replicated to a secure, immutable cloud storage provider.
This combination gives you the best of both worlds: quick recovery for minor incidents (like a deleted file) and a disaster-proof off-site copy that ransomware simply cannot touch.
The numbers prove this approach works. A remarkable 70% of organizations hit by ransomware avoided paying because they could restore from backups. The same global study found that 97% of companies with encrypted data eventually got it back, showing how a resilient backup strategy completely yanks the leverage away from attackers. You can see more insights in the Sophos State of Ransomware report.
The Most Important Step: Testing Your Recovery
I can't stress this enough: a backup strategy is useless until you've proven you can restore from it. I’ve seen too many businesses diligently back up their data for years, only to find out the files are corrupted or the process fails when a real crisis hits.
You must conduct regular recovery drills. This doesn't mean taking your entire server offline for a day. Modern tools allow us to spin up a virtual copy of your server from a backup in a totally isolated environment. From there, we can verify that the operating system boots, applications run, and your critical files are actually accessible.
Our Pro Tip: Schedule recovery tests at least quarterly, and always test after any significant changes to your IT environment. The peace of mind that comes from knowing—not just hoping—that your recovery plan works is invaluable.
This proactive testing turns your backup system from a passive insurance policy into an active, verified recovery solution. For more guidance on strengthening your defenses, you can explore some of our other cybersecurity tips for small businesses.
This simple diagram outlines how patching and segmenting your network are foundational steps that come even before backups. They're about reducing your attack surface from the get-go.
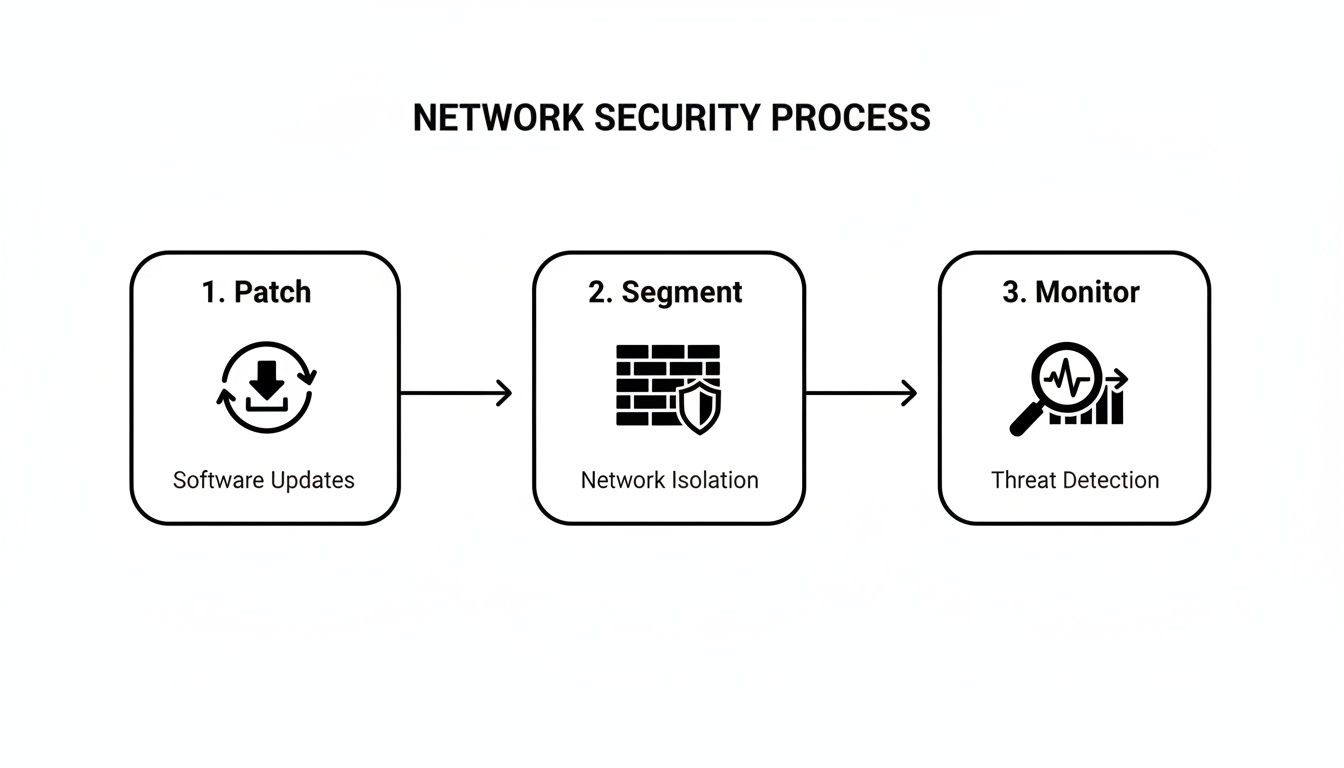
It really underscores that security is a process. You close known vulnerabilities (patching) and contain potential breaches (segmentation) as critical first steps in a layered defense.
Creating Your Incident Response Playbook
Let's be realistic. Even with the best defenses, a determined attacker might one day find a way through. When that happens, your biggest enemy isn't the malware itself—it's the chaos, confusion, and panic that follows.
An Incident Response (IR) Playbook is your antidote to that chaos. Think of it as a pre-written, step-by-step guide that turns a high-stress crisis into a calm, methodical process.
For a small or midsize business in Western PA or Eastern OH, this plan doesn't need to be a hundred-page document. It just needs to be clear, easy to find, and actionable. Your team needs to be able to grab it and act decisively to stop the bleeding and get back to business fast.
Defining Key Roles and Responsibilities
When a breach is discovered, the first question everyone asks is, "Who's in charge?" Your IR playbook must answer that immediately. Trying to figure out roles and responsibilities in the heat of the moment is a recipe for disaster.
Before an incident ever happens, you need to clearly define the core members of your Incident Response Team. This isn't about giving people a new full-time job; it’s about assigning specific duties for when they're needed most.
- The Decision-Maker: This is usually the business owner, CEO, or another senior leader. Their job is to make the big calls: Should we contact law enforcement? Do we approve emergency spending for recovery services?
- The Technical Lead: This is your internal IT manager or, more often for SMBs, your main contact at your IT partner (like us at Eagle Point). They're the ones in the trenches, leading the technical effort to contain and eradicate the threat.
- The Communications Lead: Often someone from HR or marketing, this person manages all messaging, both internal and external. They ensure employees, customers, and other stakeholders get clear, consistent information without spreading panic.
Getting these roles locked down ahead of time kills confusion and makes sure every critical function is covered from the start.
Our Pro Tip: Print a physical copy of your IR plan. Make sure it includes contact information for your team, your IT provider, your lawyer, and your cyber insurance carrier. In a full-blown ransomware attack, your digital files and network access could be completely gone.
Your Immediate Action Checklist
The first 60 minutes of a response are absolutely critical. Your playbook needs a simple, straightforward checklist of what to do the second a breach is suspected. This prevents knee-jerk reactions that can—and often do—make the problem worse.
Your first moves should be all about containment.
- Isolate the Affected Device(s): The number one priority is to stop the spread. Immediately disconnect the computer or server you think is infected from the network. Do not shut it down unless your IT pro tells you to, as this can destroy valuable evidence. Just unplug the network cable or turn off the Wi-Fi.
- Contact Your IT Partner: Your very next move should be a call to your managed service provider. Their security team has the tools and experience to properly assess what’s happening and kick off the technical response.
- Preserve Evidence: Start documenting everything. Take photos of any ransomware notes on computer screens. Write down the exact time you discovered the issue and which systems are acting strangely. This information will be vital for the investigation.
- Do Not Attempt DIY Recovery: It’s tempting to try and delete suspicious files or run an antivirus scan yourself. Resist the urge. You can easily make things worse by spreading the infection or overwriting crucial forensic data. Wait for the experts.
Post-Incident Review and Improvement
Once the immediate threat is neutralized and your systems are back online, the job isn't over. A huge part of preventing the next attack is learning from the one that just happened. Your playbook needs a process for a post-incident review.
This means sitting down as a team and asking some tough questions:
- How did the attacker get in?
- What specific vulnerability did they exploit?
- What parts of our response plan worked well?
- Where did we struggle or run into delays?
The answers will shine a light on the gaps in your security. Maybe you need more training on a new type of phishing email, or perhaps a piece of software has a vulnerability that needs to be patched immediately. This feedback loop turns a painful event into a powerful opportunity to make your defenses stronger.
Making Smart Security Investments on an SMB Budget
For a small business, every dollar has a job to do. Cybersecurity can often feel like a black hole for cash—a constant tug-of-war between protecting against digital threats and paying for concrete needs like new equipment or payroll. It's a balancing act I see every single day with the businesses we partner with across Western Pennsylvania and Eastern Ohio.
Here’s the thing: effective cybersecurity isn't about buying the most expensive tool on the market. It’s about making smart, strategic investments that give you the biggest return in actual risk reduction.
You absolutely do not need an enterprise-sized budget to build a formidable defense. The key is to get the fundamentals right first. Before you even think about chasing some niche, high-cost software, make sure your budget fully covers the non-negotiables: a rock-solid backup and recovery solution, employee training that actually sticks, and Multi-Factor Authentication rolled out everywhere it can be.
The Real Value of a Managed Service Partnership
For most small and midsize businesses, the biggest security gap isn't a piece of technology—it's people. Specifically, the lack of specialized cybersecurity expertise on staff. Let's be realistic: hiring a full-time, experienced security professional is off the table for many, with salaries easily clearing six figures before you factor in benefits and tools.
This is where partnering with a Managed Service Provider (MSP) completely changes the game.
An MSP gives you access to an entire team of security specialists for a predictable monthly fee—a fraction of what it would cost to hire a single expert. It’s not just about saving money, though. A good partnership brings serious advantages to the table:
- 24/7 Monitoring: Cyberattacks don’t punch a clock. An MSP watches your network around the clock, ready to detect and shut down threats the second they appear, whether it's 2 PM on a Tuesday or 2 AM on a Sunday.
- Proactive Management: We take on the critical but tedious work that often gets pushed aside. Think patch management, verifying your backups actually work, and fine-tuning security rules. This frees up you and your team to focus on what you do best: running your business.
- Strategic Guidance: A true MSP partner does more than just fix things when they break. We act as your virtual Chief Information Officer (vCIO), helping you build a smart, long-term technology roadmap that aligns with your actual business goals and budget.
The right MSP transforms cybersecurity from a reactive, unpredictable expense into a proactive, strategic advantage. It’s hands-down the most efficient way for an SMB to get enterprise-level security muscle without the enterprise-level price tag.
By working with an MSP, you're not just buying a service; you're gaining a partner dedicated to keeping you ahead of the curve. You can finally ensure your technology investments are smart, secure, and built to support your company's growth.
Your Top Ransomware Prevention Questions, Answered
I get it. We've covered a lot of information, and you're probably wondering how these strategies translate to your specific business in Western PA or Eastern OH. That’s a good thing. Asking the right questions is the first step toward building a real defense. Let's tackle some of the most common ones I hear from business owners just like you.
"Is Cybersecurity Insurance Enough to Protect My Business?"
This is a big one. While cybersecurity insurance is an important piece of your risk management puzzle, it's absolutely not a replacement for strong defenses. Think of it like having fire insurance on your building—you wouldn't cancel the alarm system or get rid of the fire extinguishers, right? Same principle.
In fact, getting a policy today is tougher than ever. Insurers now have strict checklists, and they often won't even give you a quote unless you can prove you have foundational controls like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), tested backups, and ongoing employee security training.
Insurance is there to help with the financial fallout after a disaster. It does nothing to prevent the operational chaos, lost productivity, and damaged reputation that can bring a small business to its knees. Prevention will always be the smarter, more cost-effective move.
"Is My Small Business Really a Target for Ransomware?"
Yes. Emphatically, yes. The nightly news is filled with stories about massive corporations getting hit, which makes it easy to think, "Why would they bother with me?" But cybercriminals see SMBs as the ideal target: valuable enough to pay a ransom but often without the robust security of a large enterprise.
They aren't sitting in a dark room picking your company's name out of a hat. They use automated bots to constantly scan the internet for any weakness, regardless of company size.
It’s not personal; it's automated. Attackers aren't hand-picking you—their software is scanning for any open digital door. If your business relies on data to operate, you are a potential target.
This is why being proactive is non-negotiable for businesses of any size. For a deeper look at common concerns and practical advice, you can find some additional insights on preventing ransomware attacks.
"How Can I Implement Better Security with a Limited Budget?"
This is the most practical and important question of all. The good news is, you don't have to break the bank to make a huge impact. The key is prioritizing.
Start with the high-impact, low-cost fundamentals. Turning on MFA for your key applications is often free or already included in software you pay for, like Microsoft 365. A solid employee training program costs very little but delivers an incredible return by turning your team into a human firewall.
When it comes to the more advanced capabilities—like 24/7 network monitoring, threat hunting, and expert incident response—partnering with a Managed Service Provider (MSP) is hands-down the most cost-effective route. It gives you an entire team of security specialists for a predictable monthly fee, which is a fraction of the cost of hiring even one full-time cybersecurity expert in-house.
Trying to navigate the complexities of cybersecurity on your own can feel overwhelming. At Eagle Point Technology Solutions, we serve as your dedicated IT partner, building a practical security roadmap that respects your budget and protects your business. If you're ready for a clear, no-nonsense conversation about securing your company's future, let's talk. Contact us today for a complimentary security consultation.